How to Spot Fake Anti-Virus Software
This is a very good article on Fake Anti-virus software and it’s implications.
Take the time to read it and you may prevent the pain of Identity Theft and Credit Card Fraud!!!
Article by Sue Marquette Poremba
Fake anti-virus (AV) software is a pain in the rear. It’s annoying as all get-out. And it can do a lot of damage to your computer. Just when you think you’ve figured out that it’s fake, the bad guys make changes.
If you’re lucky enough to have never experienced fake AV, it usually arrives as a piece of malware that pops up on your screen with a dire warning that your computer is infested with viruses — a lot of them.
If you click on the button, it offers to download the AV software to “clean” your computer. But that’s not a good idea.
“There are many versions of fake AV currently circulating on the Internet today,” said Raul Alvarez, senior security researcher for Fortinet’s FortiGuard Labs in Sunnyvale, Calif. “While there are different variations, styles and names, they all share a common feature set.”
Anatomy of a scam
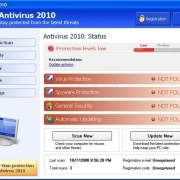
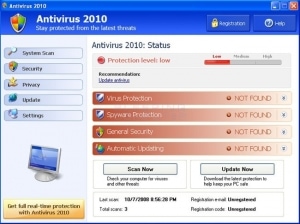
The first feature is a professional-looking graphical user interface that makes it look like a legitimate anti-virus application. Once the fake AV gets into a user’s computer system, it launches the interface and pretends to begin “scanning” the computer.
Once the “scan” is finished, fake AV typically tells the user that the system is riddled with malicious software
Next comes the crucial part: The fake AV wants payment in order to “clean” the system of all that bogus malware.
But don’t enter that credit-card information. Once you do, all that data gets shipped off to Eastern Europe or Brazil, and you immediately become a prime candidate for identity theft.
Even worse, some fake AV loads real malware, meaning you’ve just paid to have your computer infected, and others log your keystrokes or try to steal other information from your machine.
[8 Security Basics the Experts Want You to Know]
The new breed
Alvarez and his colleagues recently found a new variant of fake AV that’s got a brand-new look. They’ve given it the catchy name of W32/FakeAV.RA!tr.
“Once the malware is installed, an infected user receives a warning message that reads the software has discovered a spyware infection,” Alvarez said.
The warning balloon looks like it’s coming not from some random anti-virus software that you’ve never heard of, but from the real anti-virus package you’ve already installed. That’s pretty sneaky.
The next part of the scam is par for the course.
“When a user clicks on this warning message, a new application window that resembles a legitimate anti-virus application appears, starts ‘scanning’ the system and begins displaying detected infections,” Alvarez said.
“Once the detection phase is complete, a new window appears that displays the number of infections the software has discovered. The window also includes an option for the user to remove the detected threats or ‘Continue unprotected.’ Common sense dictates a user selects remove the ‘threats.'”
If you continue to click through, you’ll next be asked for your credit-card information and you are taken to a checkout screen. Then things get bad.
“This version of fake AV displays a warning message whenever a user tries launching a program and is particularly nasty as it doesn’t allow a user to launch any applications from their computer,” Alvarez said.
How to protect yourself
Computers are infected with fake AV through infected email attachments, links within emails or social-media links that lead users to malicious sites that automatically infect PCs and Macs via drive-by downloads.
The trick to avoiding fake AV infection is to know what’s already on your system. You should already have genuine anti-virus software that you’ve personally bought or installed.
Alvarez recommended being familiar with your anti-virus software and to know what it looks like when prompts you for an update, if it isn’t done automatically.
If an update or scan prompt doesn’t match your regular anti-virus software prompt, fake AV has most likely made its way onto your computer.
“Don’t forget, you already paid for the software on your computer,” Alvarez said, “so if you are being asked to pay for something, it is fake.”
If you do end up with fake AV on your system, be assured that you aren’t alone — this is a billion-dollar business for criminals.
First, scan your computer with your legitimate anti-virus software. If it’s blocked by the fake AV, reboot your computer in “safe” mode and scan again.
“In addition, it is advised to do an ‘offline scan,” Alvarez said. “This means a computer should to be scanned and cleaned outside of the full operating system to complete remediation.
“This requires a restart into the Windows Pre-installation Environment (WinPE) to run a scanning utility, such as Windows Defender Offline scan tool,” he added.
Article Source: Security News Daily



 Melbourne, 28 May 2010 – AVG (AU/NZ) Pty Ltd warns that Apple Macs running the OS X operating system, or some flavour of Linux distribution, are not immune to viruses, malware and other forms of Internet-carried spambots, Trojans, hacking and phishing.
Melbourne, 28 May 2010 – AVG (AU/NZ) Pty Ltd warns that Apple Macs running the OS X operating system, or some flavour of Linux distribution, are not immune to viruses, malware and other forms of Internet-carried spambots, Trojans, hacking and phishing.